SoifGo Tutorial: How effects work
Simulation Setup
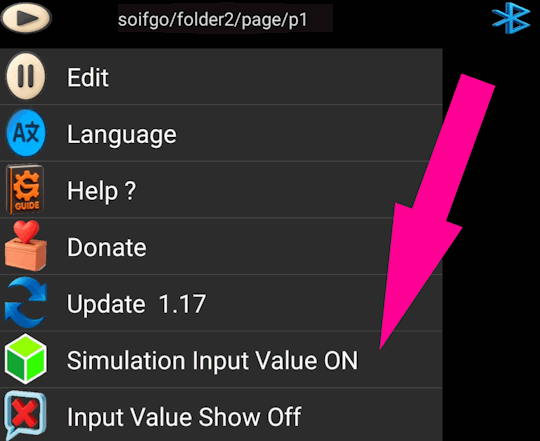
If the required hardware for applying values by address to test button actions is unavailable,
you can enable the simulator. It provides an internal counter ranging from 1 to
1024 at address 123, allowing you to prototype and test your button behavior.
How to Use
- Set the button behavior to numeric input (Bluetooth or API or MQTT ).
- Assign address
123and maximum input value1024. - Enable Simulation Input Value from the Play menu.
- The simulator will apply values from
1to1024automatically. - Once testing is complete, configure the external hardware address as needed.
Setup
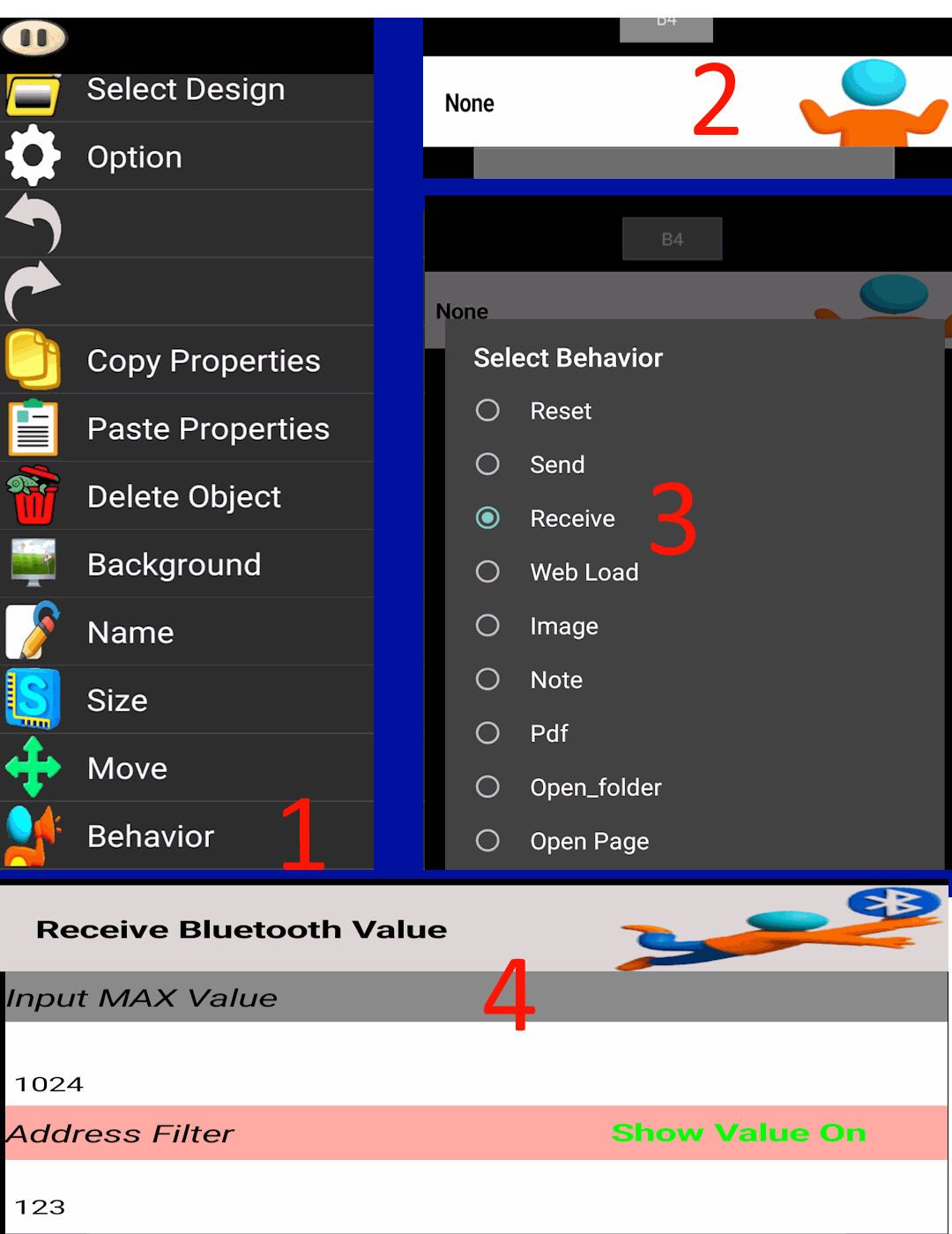
- Create the button: Set behavior to numeric input (Bluetooth or API or MQTT).
- Address:
123. Maximum:1024. - Enable simulator: Use simulation input value in Play to generate values
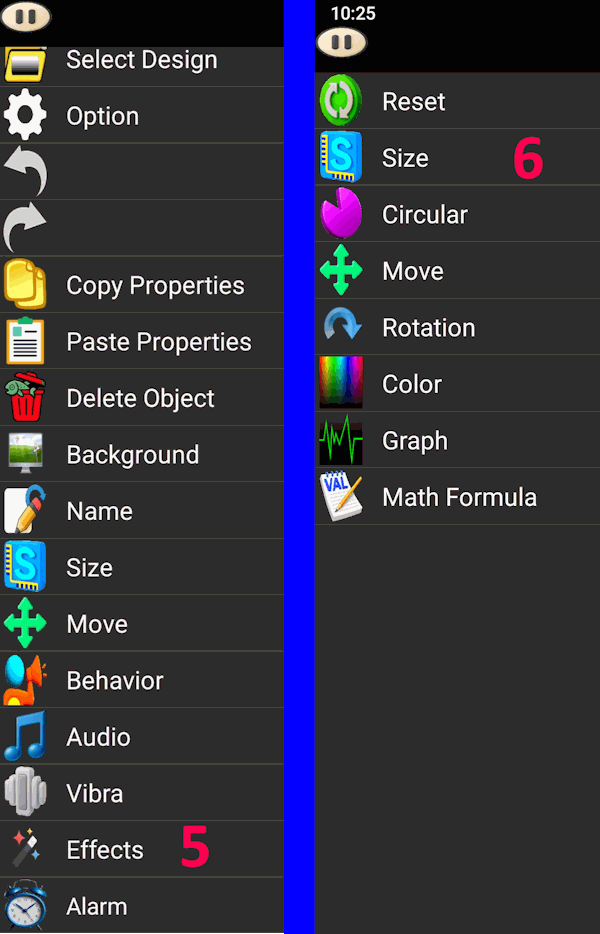
1 → 1024. - Edit mode: Click the button and open Effects. Options include Size, Circle, Move, Rotate, Color, Graph, Formula.
Size
Two sliders appear: the upper slider sets width to the far right; the next slider sets height to the top. For maximum variation,
place the button at the leftmost and lowest position. With numeric input in Play, the button scales from its initial size to the
configured maximum in proportion to the input (up to 1024).
Suitable for balancing visuals like rising water or fuel level, or any growing variable.
Circle
Renders a circular chart (full or partial) behind the button. Set start and end degrees for the minimum and maximum input. Adjust the button’s background for visibility. Ideal for showing input power, throttle, and similar gauges.
Move
Moves the button to the far right and to the top based on input. Two sliders control motion: the first for horizontal (right), the second for vertical (up). Useful for building thermometers, balancers, scales, tank level, and similar indicators.
Rotate
Rotates the button up to 360° for maximum input. The first slider sets the start position for input 0;
the second sets the end rotation at maximum input. If you are using a needle in the button background and cannot reach a specific
position, adjust the initial needle/background rotation after setting the background to achieve the target angle.
Suitable for clocks, pressure/temperature/current/voltage gauges, speedometers, and more.
Color
Predefined options include battery, cooling, brightness, red, green, blue, and yellow. Each has specific use cases—for example, battery visualizes depletion, and red increases in intensity from minimum to maximum input.
Size Circular Move Rotation Color Math Furmula
Graph
Draws a line graph for the input on the button. In settings, select graph line color and thickness. In the trigger section you have four options:
- Phone/internal timing with saving
- Internal timing without saving
- External trigger with saving
- External trigger without saving
For external triggers, each input stores both the value and time—ensure your sending cadence is correct (e.g., per second or hourly),
since transmission errors affect recorded time. At the bottom, two sliders are available: the first sets internal timing from
100 ms to 48 s; the second controls graph line thickness. Graphs are saved in the SoifGo folder and can
be shared or transferred. In Play, you can zoom and navigate history pages.
If you want to create another graph or a new group using the same button, simply change the button name in the Edit section. With the new name, fresh graphs will be recorded. To revisit a previous graph, rename the button back to its former name. Don’t worry if you forget—graphs are stored under their names in the SoifGo/graph folder. Use your file manager to browse and access them anytime.
Graph
Formula
This feature displays a custom value derived from the input. For example, if input range is 0–1024 but you want
0–512, write val/2. The input variable name is val. Formula authoring uses HTML-like
functions.
Available Math Functions with Examples
| Function | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
+ | Adds two numbers | val+10 → if val=5 → 15 |
- | Subtracts second number from first | val-2 → if val=7 → 5 |
* | Multiplies two numbers | val*3 → if val=4 → 12 |
/ | Divides first number by second | val/2 → if val=10 → 5 |
% | Remainder of division | val%3 → if val=10 → 1 |
Math.pow | Exponentiation | Math.pow(val,2) → if val=4 → 16 |
Math.sqrt | Square root | Math.sqrt(val) → if val=9 → 3 |
Math.cbrt | Cube root | Math.cbrt(val) → if val=8 → 2 |
Math.round | Rounds to nearest integer | Math.round(3.6) → 4 |
Math.floor | Rounds down | Math.floor(3.9) → 3 |
Math.ceil | Rounds up | Math.ceil(3.1) → 4 |
Math.trunc | Removes decimal part | Math.trunc(5.7) → 5 |
Math.fround | Rounds to 32-bit float | Math.fround(1.337) → 1.337000012 |
Math.abs | Absolute value | Math.abs(-7) → 7 |
Math.sign | Sign of number | Math.sign(-5) → -1 |
Math.random | Random number 0–1 | Math.random() → e.g. 0.42 |
Math.PI | Pi constant | Math.PI → 3.14159… |
Math.E | Euler's number | Math.E → 2.718… |
Math.sin | Sine of angle | Math.sin(Math.PI/2) → 1 |
Math.cos | Cosine of angle | Math.cos(0) → 1 |
Math.tan | Tangent of angle | Math.tan(Math.PI/4) → 1 |
Math.log | Natural log | Math.log(Math.E) → 1 |
Math.exp | e^x | Math.exp(1) → 2.718… |
Math.hypot | Hypotenuse length | Math.hypot(3,4) → 5 |
Math.max | Maximum | Math.max(1,9,3) → 9 |
Math.min | Minimum | Math.min(1,9,3) → 1 |
Math.clz32 | Leading zeros in 32-bit | Math.clz32(1) → 31 |
toRadians | Degrees → radians | toRadians(180) → 3.14159… |
toDegrees | Radians → degrees | toDegrees(Math.PI) → 180 |
ALARM
The alarm provides both text and sound notifications. It is triggered when the measured value becomes greater or less than the configured threshold. Alarm Value: The numeric threshold that activates the alarm. Alarm Message: The text notification displayed when the alarm is triggered. Alarm Option: Can be enabled for either "greater than" or "less than" conditions. Delay Setting: A configurable delay bar is available at the bottom to manage consecutive alarms. Sound Notification: The alarm sound uses the same configuration as the button sound setting.